Introduction:
This article will explore the critical role of utility monitoring in industries and facilities. We'll discuss the objectives it can achieve. Typically Utilities include electricity, water, compressed air, hot and cold water, steam, brine, and nitrogen. These utilities are often distributed from a central location to production lines
Objective
The main Objectives for Utility Monitoring
- Ø Ensure a continuous supply of utilities.
- Ø Maintain all utilities within their specified ranges throughout the facility.
- Ø Monitor consumption and address waste to improve efficiency.
- Ø Optimize production planning to avoid over or underutilization of resources.
- Ø Reduce breakdowns by monitoring assets like compressors, boilers, pumps, and motors to identify and address potential issues.
- Ø Support sustainability and net-zero goals through effective utility management.
Existing Systems/Solutions
Industries typically employ different software systems from various vendors to manage their resources. This fragmentation, often involving SCADA or desktop applications accessible only to limited personnel, can lead to cumbersome tasks like juggling multiple systems and correlating data. These systems often provide only surface-level information, such as daily and monthly consumption, and may not be readily visible to production floor staff.

Implementation
For success of any project the objectives of the customer should be carefully analysed understand the Parameters need to be monitored.
There are Three main systems in Utility Monitoring
- 1) Measurement: Which includes Instruments, Sensors or existing PLCs.
- 2) Transmission/Integration: which includes Gateways, Converters, Scanners typically to convert Sensors/Instrumentation data to a standard protocol
- 3) Software, Analysis/ Display: Receives data from different sources and present in required Business requirement
Challenges:
1) Selecting the right sensors/instruments for the given field condition
2) Integrating with the existing PLCs/Instruments
3) Adapting right system architecture and time to implement
4) Project costing and Return on Investment
5) Multple stake holders who includes different Departments on Customer side like IT, Engineering, Maintenance, Finance and also on suppliers.
6) Technical Challenges: We need to understand the functionality and how to integrate Instrumentation, Sensors, PLCs from field to Software.
On the whole Customer needs a Implementation Partner who understands from the Field Instrumentation to the Software.
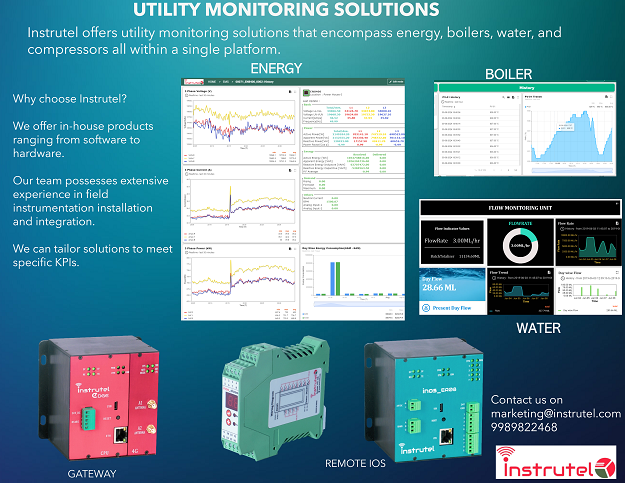
Advantages with Instrutel:
Instrutel is having expertise in design, development and deployment of Instrumentation and Software. We have a full stack of in-house technology developed inhouse there by decreasing the number of stake holders and ability to deploy solution in short span of time. Our Hardware platforms are customizable and Ready to deploy.
Our products include:
1) Remote Ios for integrating various type of Sensors. Instrutel INOS series will connect to Analog and Digital sensors in the field.
2) Gateways: Gateways can connect existing PLCs, Instruments to the software.
3) Software: Our Web-Based applications and Mobile applications can be Tailored to any Business logic. It can support on-premise or cloud-based deployment based on the customer requirement.
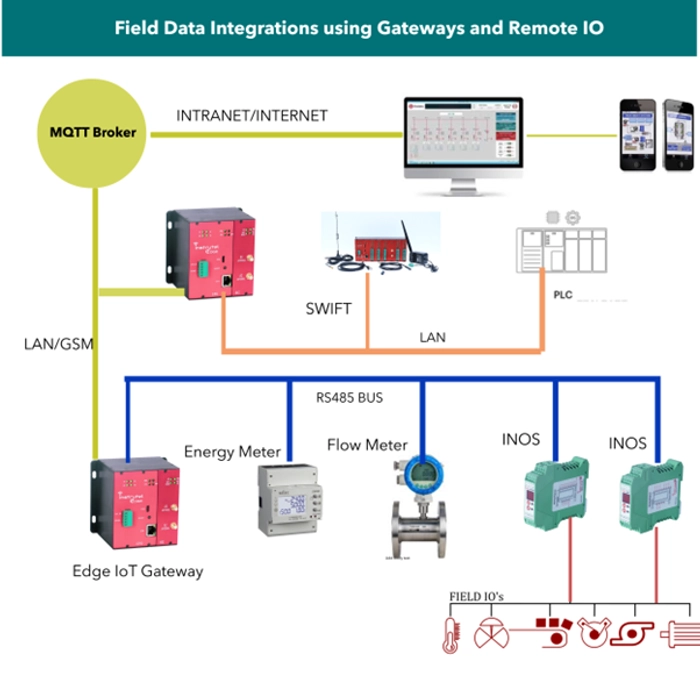
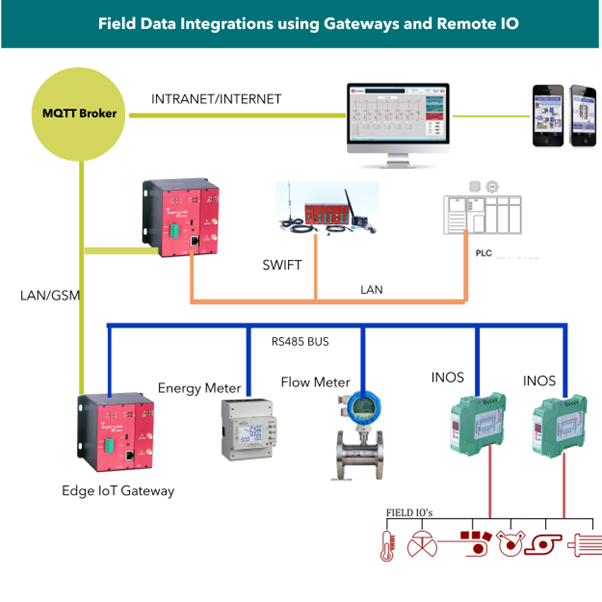
Architecture:
Here is the typical System architecture for the Utility Monitoring System.
Conclusion:
By providing real-time data access and use of right technology Utility Monitoring will drive efficiency. Having a right implementation partner with right support is essential for overcoming challenges and achieving right objectives for the multiple stakeholders.